By Sayon Deb, Director of Insights, UL Requirements & Engagement
In simply 5 years, lithium-ion battery fires linked to e-mobility gadgets have developed from a fringe danger right into a mainstream security and legal responsibility disaster – significantly in dense city areas, like New York Metropolis, the place adoption of those gadgets has outpaced regulatory safeguards.
Along with the plain public security menace, e-mobility battery associated fires signify a major and increasing legal responsibility publicity for insurers, property managers, and metropolis companies. Our newest report – developed in collaboration with Oxford Economics – units out to reply a extra elementary query: What is that this disaster actually costing town?
The reply, conservatively estimated, is as much as $519 million in mixed human and financial loss between 2019 and 2023. This determine consists of fatalities, accidents, and structural property harm
Why Now? Why New York?
The dramatic rise in hearth incidents – an estimated eightfold enhance from 21 in 2019 to as many as 187 incidents in 2023 – correlates strongly with the inflow of low-cost, uncertified e-bikes and scooters. New York Metropolis’s distinctive mixture of visitors congestion, delivery-based gig work, and dense multi-family housing has made it a case examine in how rapidly innovation can outstrip danger administration.
Information from the Hearth Division of New York, the Client Product Security Fee, and UL Options’ Lithium-Ion Battery Hearth Incident Database fashioned the inspiration of our modeling. This helped us generate incident estimates of fatalities, accidents, and structural properties damages.
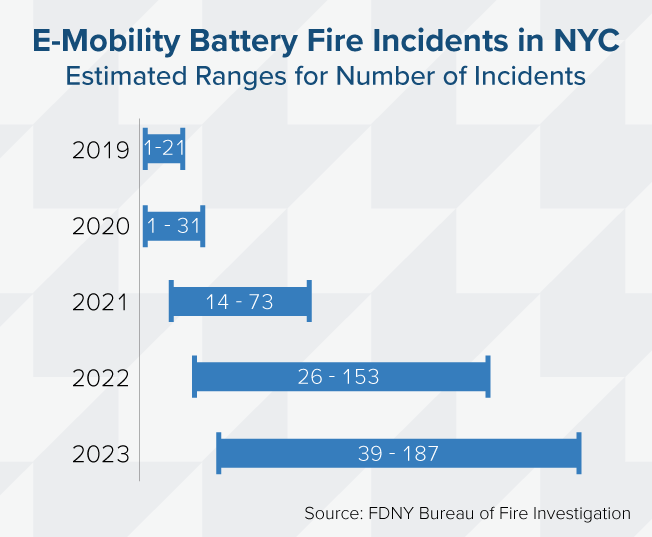
Oxford Economics translated these incident stories into price estimates utilizing a rigorous, conservative methodology by making use of federal valuation metrics for lack of life and harm. Fatality prices have been calculated utilizing the U.S. Division of Transportation’s Worth of a Statistical Life, set at $13.2 million per life as of 2023. Non-fatal harm prices have been derived as severity-weighted fractions of that worth, starting from minor harm to essential harm, in accordance with DOT and Workplace of Administration and Price range financial steering.
Our evaluation then built-in structural hearth price benchmarks from each Triple-I and the Nationwide Hearth Safety Affiliation. Triple-I’s information was significantly vital in defining the upper-bound estimates for property loss. Claims information on the typical insurance coverage payout for residential hearth harm supplied a grounded, actuarial counterweight to NFPA’s generalized nationwide averages.
This dual-source method allowed us to seize a extra life like vary of doubtless losses throughout completely different housing varieties, from NYCHA public items to personal properties.
A rising blind spot for insurers
From a risk-modeling standpoint, e-mobility hearth incidents don’t map simply to standard insurance coverage classes. Many e-mobility customers, significantly gig financial system employees, depend on leased, used, or modified e-bikes and e-scooters to fulfill supply calls for. A few of these gadgets are powered by third-party or uncertified batteries or, in some cases, include second-hand elements. This creates a messy danger surroundings through which it’s onerous to know who owns what, the way it has been maintained, or the way it’s getting used. Furthermore, fires ensuing from these gadgets typically fall exterior the scope of normal product warranties or producer accountability. This makes it tough to find out who’s accountable when one thing goes unsuitable.
For insurers, this presents a rising blind spot. Conventional assumptions round property and contents protection didn’t embody high-risk gadgets charged in hallways or shared residing areas or for ignition sources that aren’t a part of standard product recall channels.
A $300 imported battery with no certification can set off a six-figure declare, and people dangers have gotten extra widespread.
The Path Ahead
Regulatory momentum is enhancing. New York Metropolis’s Native Regulation 39, signed in 2023, bans the sale and lease of uncertified e-mobility gadgets. In July 2024, New York Governor Hochul enacted further statewide measures to assist battery security and person training. Federal laws aimed toward establishing nationwide security necessities for lithium-ion batteries utilized in e-bikes and e-scooters is making its manner by means of Congress. Whereas these are constructive steps, enforcement and consciousness stay uneven, leaving vital gaps in shopper safety and danger mitigation.
From our perspective at ULSE, a multi-pronged technique is important:
- Higher enforcement of security requirements for batteries and chargers.
- Extra sturdy public training on protected charging practices.
- Commerce-in and swap applications that encourage supply employees to discard unsafe batteries.
- Underwriting fashions that think about system certification, shopper conduct, and constructing kind.
- Improved incident reporting frameworks that allow cities and insurers to gather higher information and due to this fact higher monitor danger publicity.
With higher information, smarter requirements, and extra coordinated public-private motion, the way forward for e-mobility will thrive with security at its middle.
Mr. Deb will likely be among the many danger and insurance coverage trade thought leaders talking at Triple-I’s Joint Business Discussion board (JIF) in Chicago on June 18, 2025. It’s not too late to register to attend this insight-driven occasion.

